Galvanized Aircraft Cable
How does aircraft cable differ from wire rope?
Aircraft cables are available in smaller diameters than wire rope. For example, aircraft cables are available in 3/64 in. diameter while most wire ropes begin at a 1/4 in. diameter.
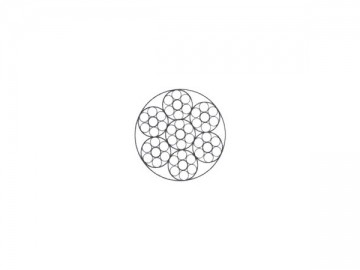
Aircraft Cable Description: The Galvanized Steel Aircraft Cable has a 7x19 construction. The 7x19 construction consists of 1 core cluster of 19 strands of cable surrounded by 6 clusters of 19 strands of cable (see picture of cross section below). This aircraft cable is more flexible than 1x7, 1x19, or 7x7 construction. The aircraft cable is very flexible for creating loops and has a low fatigue rate for use with pulleys and sheaves.
The galvanized aircraft cable is zinc coated for weather resistance and durability. The coating can be scratched, however, under heavy-duty use and the galvanized cable is therefore best suited as safety or securing line that is not exposed to any wear and tear or for short-term applications where rust is not a concern.
About Galvanized Aircraft Cable
Quality: This aircraft cable has industrial-use quality and strength. It is stronger and more durable than a standard home-use wire rope cable. The aircraft cable is manufactured in according to Federal Specification RR-W-410E and A.S.T.M. A 1023/A 1023M, as applicable.
Accessories: Use optional thimbles and rope clips to secure the wire rope.
Industry designation: While users often freely interchange the words aircraft cable and wire rope, professional users make the following differentiation: Wire rope is generally used for lifting, aircraft cable is not.
Warning: The air craft cable is Not for use with aircraft controls and Not for lifting or suspending of loads!
What you should know BEFORE you buy!
Aircraft Cable Educational Content
Learn: Galvanized vs. Stainless Steel Aircraft Cable
When selecting aircraft cable, consider the differences between galvanized and stainless steel aircraft cable. Galvanized wire rope is zinc coated for weather resistance; however, the zinc coating can be damaged from scratches or impacts which can then lead to rust. Furthermore the galvanization does not hold up well to salt water. Consequently galvanized aircraft cable is not as durable for use is environments close to oceans or in marine applications. The galvanized wire rope is therefore best suited as safety or securing lines that do not experience any wear and tears during use or for short-term applications. The galvanized wire rope cable is also available with a vinyl coating which adds a layer of protection against weather and it also guards against any scratching of the zinc coating. In comparison, the stainless steel aircraft cable will not rust even when scratched, however, it is slightly lower in capacity (breaking strength) and it is also much more expensive. This choice is ideal for long-term durability even when exposed to rubbing and scratching.
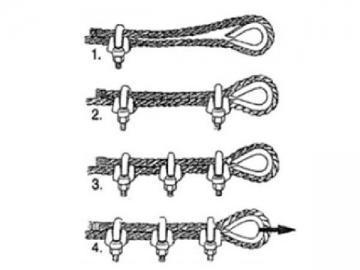
Correct Method of Installing Wire Rope Clips
When using wire rope clips to secure aircraft cable, extreme care must be exercised to make certain they are attached correctly. Failure to do so could result in serious injury or death.
1. Turn back specified length of wire rope from thimble. Put first clip one saddle width from seized "dead end" (Fig. 1 below). Seat "live end" (load carrying part) of wire rope in saddle and position U-bolt over "dead end." Remember: "Never saddle a dead horse." Tighten nuts evenly to proper torque (see tables on next two pages).
2. Put second clip close to the thimble without binding it (see Fig. 1). Install nuts firmly but do not yet tighten to proper torque.
3. Install all remaining clips equally spaced between the first two clips (Fig. 3). Install nuts firmly but do not yet tighten to proper torque.
4. Apply light tension to wire rope assembly, and then tighten all nuts evenly to proper torque (Fig. 4).
Inspect the wire rope clip nuts before and after each use and re-torque as needed. When loads are applied to the aircraft cable, the wire rope will stretch slightly causing the rope to slip and the termination to come loose, which may cause serious injury or death. Add at least one more clip if a pulley (sheave) is used in place of a thimble. If uncertain, check with the wire rope manufacturer. If more clips are used than specified, proportionally increase the amount of wire rope that is turned back. When the required minimum number of clips is installed in accordance with these written instructions, they will develop up to 80% efficiency when used on right lay wire rope of classes 6x19, 6x36, 7x19, 8x19, 19x7, and cable laid. Drop forged wire rope clips are recommended for use only with steel core aircraft cables.
Select the right wire rope clip for your aircraft cable application
NEVER use cast malleable wire rope clips for lifting or suspending ANY load.
Match the same size wire rope clip to the same size aircraft cable diameter. For example, use a 3/8" wire rope clip with a 3/8" wire rope aircraft cable.
When working with coated wire cable, ALWAYS
Match wire rope clip size to uncoated aircraft cable diameter and
Strip coating off aircraft cable where wire rope clips will be attached.
Install wire rope clips correctly
Never use fewer than the minimum number of wire rope clamps.
Wire rope clips are made for use with wire rope aircraft cable only. Never use wire rope clips on pipe, rod, chain, fiber rope, etc.
Use wire rope clips properly
Never connect two ends of aircraft cable with wire rope clips.
Never shock or impact load.
Inspect and maintain wire rope clips regularly
Inspect wire rope clips before each use. Discard and replace wire rope clips that are worn, distorted, or damaged.
Inspect wire rope clip nuts before and after each use and re-torque as needed.
Industry Designation
While users often freely interchange the words aircraft cable and wire rope, professional users make the following differentiation: Wire rope is generally used for lifting, aircraft cable is not.
| 1×7 | 1×19 | ||||||||
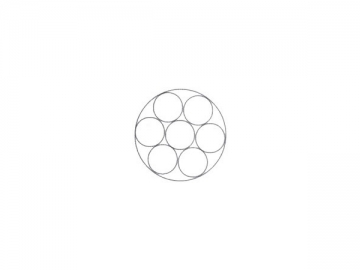 | 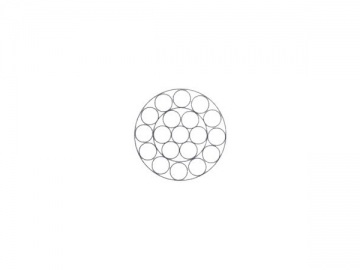 | ||||||||
| Nominal Diameter | Nominal T/S | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Cross Section | Approximate Weight | Nominal Diameter | Nominal T/S | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Cross Section | Approximate Weight |
| mm | N/mm | KN | mm | kg/100M | mm | N/mm | KN | mm | kg/100M |
| 0.70 | 1870 | 0.54 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 1870 | 1.01 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| 1.00 | 1870 | 1.08 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 1.20 | 1770 | 1.37 | 0.86 | 0.90 |
| 1.50 | 1770 | 2.18 | 1.37 | 1.20 | 1.40 | 1770 | 1.86 | 1.17 | 1.20 |
| 1.80 | 1770 | 3.15 | 1.98 | 1.80 | 1.70 | 1770 | 2.74 | 1.72 | 1.70 |
| 1.95 | 1770 | 3.70 | 2.32 | 2.10 | 2.00 | 1770 | 3.81 | 2.39 | 2.40 |
| 2.50 | 1770 | 5.94 | 3.73 | 3.70 | |||||
| 3.00 | 1670 | 8.07 | 5.37 | 5.40 | |||||
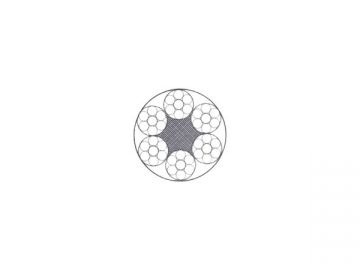
| 6×7 IWS | 6×7 NF | ||||||||
 |  | ||||||||
| Nominal Diameter | Nominal T/S | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Cross Section | Approximate Weight | Nominal Diameter | Nominal T/S | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Cross Section | Approximate Weight |
| mm | N/mm | KN | mm | kg/100M | mm | N/mm | KN | mm | kg/100M |
| 1.80 | 1870 | 2.53 | 1.54 | 1.50 | 1.80 | 1960 | 2.28 | 1.32 | 1.40 |
| 2.15 | 1870 | 3.65 | 2.22 | 2.20 | 2.15 | 1960 | 3.28 | 1.90 | 2.00 |
| 2.50 | 1870 | 4.97 | 3.02 | 3.00 | 2.50 | 1960 | 4.47 | 2.59 | 2.70 |
| 3.05 | 1870 | 7.32 | 4.45 | 4.40 | 3.05 | 1870 | 6.27 | 3.81 | 4.00 |
| 3.60 | 1870 | 10.14 | 6.16 | 6.20 | 3.60 | 1870 | 8.69 | 5.28 | 5.50 |
| 4.50 | 1770 | 14.98 | 9.62 | 9.60 | 4.10 | 1770 | 10.40 | 6.68 | 7.00 |
| 5.40 | 1670 | 20.35 | 13.85 | 13.80 | 4.50 | 1770 | 12.85 | 8.25 | 8.70 |
| 5.40 | 1670 | 17.46 | 11.88 | 12.50 | |||||
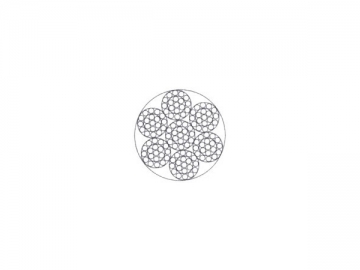
| 6×19 IWS | 6×19 NF | ||||||||
 |  | ||||||||
| Nominal Diameter | Nominal T/S | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Cross Section | Approximate Weight | Nominal Diameter | Nominal T/S | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Cross Section | Approximate Weight |
| mm | N/mm | KN | mm | kg/100M | mm | N/mm | KN | mm | kg/100M |
| 3.00 | 2026 | 7.32 | 4.18 | 4.2 | 3.00 | 2060 | 6.27 | 3.58 | 3.80 |
| 3.60 | 1770 | 9.06 | 6.02 | 6.00 | 3.30 | 1770 | 6.51 | 4.33 | 4.50 |
| 4.20 | 1770 | 12.32 | 8.19 | 8.20 | 3.60 | 1770 | 7.76 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| 5.10 | 1770 | 18.17 | 12.08 | 12.10 | 4.20 | 1770 | 10.56 | 7.02 | 7.40 |
| 6.00 | 1670 | 23.72 | 16.7 | 16.70 | 4.80 | 1770 | 12.94 | 8.60 | 9.00 |
| 7.50 | 1670 | 37.06 | 26.11 | 26.00 | 5.10 | 1770 | 15.57 | 10.35 | 10.90 |
| 8.25 | 1670 | 44.86 | 31.06 | 32.00 | 6.20 | 1670 | 20.34 | 14033 | 15.00 |
| 9.00 | 1670 | 53.37 | 37.60 | 37.60 | |||||
| 9.75 | 1670 | 62.64 | 44.13 | 44.10 | |||||
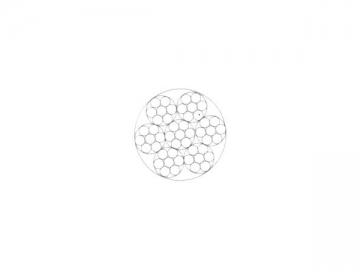
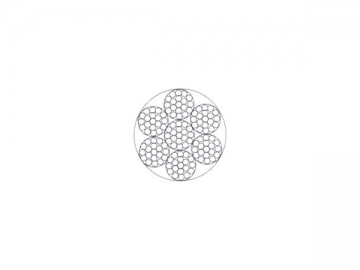
| MIL-W-83420D | ||||||||
 |  | |||||||
| Nominal Diameter | Construction | Min.Breaking load(A) (Min.b/l) | Min.Breaking load(A) (Min.b/l) | Approximate Weight | ||||
| Inch | mm | 7*7 | LB | KN | LB | KN | LB/100Inch | kg/100m |
| 3/64 | 1.19 | 7*7 | 270 | 1.20 | 270 | 1.20 | 0.42 | 0.62 |
| 1/16 | 1.59 | 7*7 | 480 | 2.14 | 480 | 2.14 | 0.75 | 1.12 |
| 3/32 | 2.38 | 7*19 | 920 | 4.09 | 920 | 4.09 | 1.60 | 2.38 |
| 3/32 | 2.38 | 7*19 | 1000 | 4.45 | 920 | 4.09 | 1.74 | 2.59 |
| 1/8 | 3.18 | 7*19 | 2000 | 8.90 | 1760 | 7.83 | 2.90 | 4.31 |
| 5/32 | 3.97 | 7*19 | 2800 | 12.46 | 2400 | 10.68 | 4.50 | 6.70 |
| 3/16 | 4.76 | 7*19 | 4200 | 18.69 | 3700 | 16.46 | 6.50 | 9.67 |
| 7/32 | 5.56 | 7*19 | 5600 | 24.92 | 5000 | 22.25 | 8.60 | 12.80 |
| 1/4 | 6.35 | 7*19 | 7000 | 31.15 | 6400 | 28.48 | 11.00 | 16.37 |
| 9/32 | 7.14 | 7*19 | 8000 | 35.60 | 7800 | 34.71 | 13.90 | 20.68 |
| 5/16 | 7.94 | 7*19 | 9800 | 43.61 | 9000 | 40.05 | 17.30 | 25.74 |
| 3/8 | 9.53 | 7*19 | 14400 | 64.08 | 12000 | 53.40 | 24.30 | 36.16 |
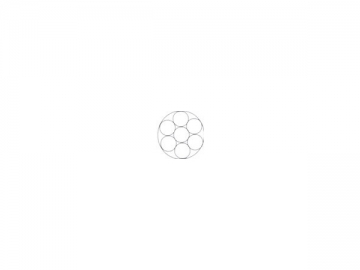 | 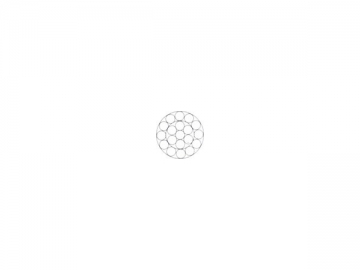 |  | 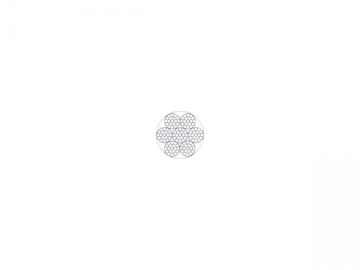 | 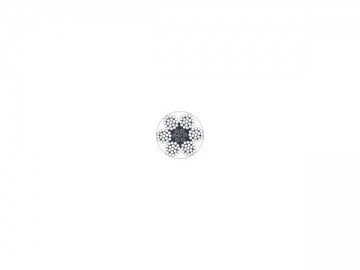 | |||||||||
| Nominal Diameter | Construction | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Approximate Weight | Nominal Diameter | Construction | Min.Breaking load (Min.b/l) | Approximate Weight | ||||||
| Inch | mm | Ib | Kg | Ib | kg | Inch | mm | Ib | kg | Ib | kg | ||
| 1/32 | 0.79 | 1*7 | 185 | 83.9 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 3/32 | 2.38 | 7*7 | 920 | 416 | 1.60 | 0.725 |
| 3/64 | 1.19 | 1*7 | 375 | 170.0 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 1/8 | 3.18 | 7*19 | 1760 | 797 | 2.90 | 1.31 |
| 3/64 | 1.19 | 1*7 | 375 | 170.0 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 5/32 | 3.96 | 7*19 | 2400 | 1090 | 4.50 | 2.04 |
| 3/64 | 1.19 | 1*19 | 375 | 170.0 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 3/16 | 4.76 | 7*19 | 3700 | 1670 | 6.50 | 2.95 |
| 1/16 | 1.59 | 1*7 | 500 | 226.7 | 0.85 | 0.38 | 7/32 | 5.56 | 7*19 | 5000 | 2260 | 8.60 | 3.90 |
| 1/16 | 1.59 | 1*19 | 500 | 226.7 | 0.85 | 0.38 | 1/4 | 6.35 | 7*19 | 6400 | 2900 | 11.00 | 5.00 |
| 5/64 | 1.98 | 1*19 | 800 | 363.0 | 1.40 | 0.63 | 9/32 | 7.14 | 7*19 | 7800 | 3530 | 13.9 | 6.30 |
| 3/32 | 2.38 | 1*19 | 1200 | 544.0 | 2.00 | 0.91 | 5/16 | 8.00 | 7*19 | 9000 | 4080 | 17.30 | 7.84 |
| 7/64 | 2.78 | 1*19 | 1600 | 725.7 | 2.70 | 1.22 | 3/8 | 9.53 | 7*19 | 12000 | 5430 | 24.30 | 11.00 |
| 1/8 | 3.18 | 1*19 | 2100 | 952.5 | 3.50 | 1.59 | 7/16 | 11.0 | 6*19 IWRC | 16300 | 7380 | 25.60 | 11.60 |
| 5/32 | 3.97 | 1*19 | 3300 | 1497.0 | 5.50 | 2.49 | 1/2 | 12.7 | 6*19 IWRC | 22800 | 10300 | 45.80 | 20.80 |
| 3/16 | 4.76 | 1*19 | 4700 | 2131 | 7.70 | 3.49 | 9/16 | 14.3 | 6*19 IWRC | 28500 | 12900 | 59.00 | 26.80 |
| 7/32 | 5.56 | 1*19 | 6300 | 2857 | 10.20 | 4.62 | 5/8 | 15.9 | 6*19 IWRC | 35000 | 15800 | 71.50 | 32.40 |
| 1/4 | 6.35 | 1*19 | 8200 | 3719 | 13.50 | 6.12 | 3/4 | 19.1 | 6*19 IWRC | 49600 | 22500 | 105.20 | 47.60 |
| 5/16 | 7.94 | 1*19 | 12500 | 5670 | 21.00 | 9.52 | 7/8 | 22.2 | 6*19 IWRC | 66500 | 30100 | 143 | 64.80 |
| 3/8 | 9.53 | 1*19 | 17500 | 7937 | 30.00 | 13.6 | |||||||
Application
Aircraft cable is used for pulling and pushing applications, and for use with pulleys, sheaves and winches. The name aircraft cable suggests uses in airplanes; however, this wire rope cable is not for use in aircrafts and Not for lifting or suspending of loads! This high strength wire rope cable is designed for pulling and securing in construction, industrial and marine applications.